History & Geography for Kids - Natural Resources of Ancient EgyptThe Civilization, Geography, Culture & History of Ancient Egypt and facts about the Natural Resources of Ancient Egypt |
|
The Natural Resources of Ancient Egypt
The Natural Resources of Ancient Egypt enabled the ancient Egyptians to become the richest and powerful civilisations of the ancient world. The Natural Resources of Ancient Egypt allowed the ancient Egyptians to thrive and to establish import and export trading with neighboring countries. The River Nile was a major natural resource enabling farming and the production of grain. The Nile River broke its banks each year, saturating the surrounding countryside with a rich fertile silt called alluvial soil that was extremely fertile and ideal for crop growing. The Natural Resources of Ancient Egypt included stone including limestone, sandstone, granite and alabaster, gold and minerals. Natural Resources also included precious and semi-precious stones including amethyst, turquoise and carnelian, copper and lead ores and flint. For additional facts and info refer to Stone Quarrying & Quarries.
Ancient Egypt - Natural Resources Fact Sheet |
Fact 1 on Natural Resources: | Nile River: The annual flooding of the River Nile enabled farming possible surrounding the banks of the river Nile, an otherwise desert region. The Nile was a source of plants such as flax and papyrus, fresh water, fish, the Nile provided mud use as a building material, attracted animals and was also an excellent means of transportation.
| Fact 2 on Natural Resources: | Flax: The Flax plant produced fiber that was made into thread and woven into linen fabric which was used to make the clothes of the ancient Egyptians.
| Fact 3 on Natural Resources: | Papyrus: Papyrus was made from the stems of a reed called cyperus papyrus was one of Egypt’s major exports.
| Fact 4 on Natural Resources: | Natron: Natron was used for mummification and also provided the gypsum needed to make plaster.
| Fact 5 on Natural Resources: | Quartzite: Quartzite is a hard white, yellow or red rock (sandstone) consisting essentially of quartz found in the Eastern and Western deserts of Egypt. It was used for statues and doorway thresholds of temples and wall linings in tombs.
| Fact 6 on Natural Resources: | Basalt: Basalt is a type of volcanic rock, very dark green, grey to black in color. It was on the floors of temples and tombs. Basalt was also used for making the black statues of Pharaohs and gods in their manifestations of jackals and cats.
| Fact 7 on Natural Resources: | Copper: Copper was an important metal because it could be easily worked and shaped into weapons and tools. Copper was used for the statues of gods and pharaohs. It was used for making tools, weapons, jewelry, amulets and statues.
| Fact 8 on Natural Resources: | Limestone: Limestone was used to cover the walls of tombs and temples and were also used to create bas relief carvings.
| Fact 9 on Natural Resources: | Malachite: Malachite is an opaque, green banded mineral which was obtained from the Sinai peninsula. Malachite was used as a mineral pigment in green paints and was ground to a fine powder and used as eye shadow.
| Fact 10 on Natural Resources: | Turquoise: Turquoise is a semiprecious stone, typically opaque and of a greenish-blue or sky-blue color. Turquoise was found in the Sinai Peninsula and was used to create, jewelry, amulets, talismans continued...
|
|
Ancient Egypt - Natural Resources Fact Sheet |
|

Stone Quarry at Tura |
|
|
Facts about the Natural Resources of Ancient Egypt
The following fact sheet provides information and interesting facts about the the Natural Resources of Ancient Egypt. 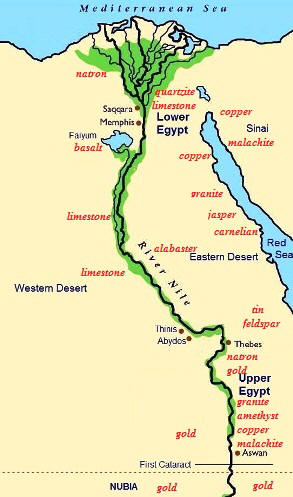
Map of Ancient Egypt Natural Resources
Ancient Egypt - Natural Resources Fact Sheet |
Fact 11 on Natural Resources: | Alabaster: Alabaster is translucent and milky white, and can be carved into beads or statues and was particularly used to create the sacred tools used during the process of mummification. Canopic jars, which housed the organs of the deceased were also made of alabaster.
| Fact 12 on Natural Resources: | Jasper: Jasper is a semiprecious stone that comes in different shades of reddish, yellow or brown. It was used to make ornamental items, jewelry, talismans and amulets.
| Fact 13 on Natural Resources: | Granite: Granite was plentiful in Upper Egypt, especially in the Aswan region. Granite came in a variety of colors including red, black, blue and gray and used for building and creating sarcophagi and statues.
| Fact 14 on Natural Resources: | Carnelian: Carnelian is semiprecious stone consisting of an orange or orange-red variety of chalcedony. Carnelian was used to create jewelry and heart and djed amulets and talismans.
| Fact 15 on Natural Resources: | Tin: Tin is a malleable, silvery metallic element obtained chiefly from cassiterite. It is used to coat other metals to prevent corrosion. Bronze is an allay of copper and tin.
| Fact 16 on Natural Resources: | Gold: Supplies of gold came from Nubia (Kush) and the Eastern desert areas of Upper Egypt. Gold was used in jewelry, amulets, talismans, masks, statues and coffins.
| Fact 17 on Natural Resources: | Feldspar: The green Feldspar stone, aka Amazonite, was used for carving images of deities. Feldspar was also the favored stone for the papyrus scepter amulet which was placed around the neck of the deceased on the day of the funeral.
| Fact 18 on Natural Resources: | Amethyst: Amethyst is a precious stone, a violet or purple variety of quartz. Amethyst was used by the ancient Egyptians as an ornament and in jewelry, amulets and talismans.
| Fact 19 on Natural Resources: | Wood: Wood was scarce in Egypt. Wood native to Egypt include palm trees, acacia, willow and sycamore. Cedarwood was imported from Lebanon and used for ships, temple doors and expensive coffins. Ebony was imported via Nubia and used for expensive furnishings and for inlays.
| Fact 20 on Natural Resources: | Ivory: Ivory was derived from an elephant or hippopotamus tusk. It sources were originally hippopotamuses in Egypt and later, elephants via Nubia and Punt. Ivory was used in carving reliefs or statues, or cut into thin sheets as inlays or veneer on furniture. continued...
|
|
Ancient Egypt - Natural Resources Fact Sheet |
|

Nile Temple at Philae |
|
Natural Resources | Facts and Information about the Natural Resources of Ancient Egypt |  | Natural Resources |  | The people, places, culture and civilization of ancient Egypt |  | Facts and information about Ancient Egypt & the Egyptians |  | Natural Resources for kids and schools |  | Natural Resources for kids, schools, homework and research |  | Natural Resources |
|
| | |
|
Facts about the Natural Resources of Ancient Egypt
Discover fast, interesting fun facts about the Natural Resources of Ancient Egypt for kids with some amazing, cool and quick information about ancient Egypt and Egyptians. Ideal for children, homework, schools, teachers and kids of all ages! Find fascinating fun facts about the Natural Resources of Ancient Egypt for kids and the history, culture and civilisation of the ancient Egyptians and ancient Egypt. Interesting, fun facts about the Natural Resources of Ancient Egypt for research, schools, students and kids of all ages.
Ancient Egypt - Natural Resources Fact Sheet |
Fact 21 on Natural Resources: | Tuff or Tuffacious limestone: The greenish colored Tuff or Tuffacious limestone was quarried in the Eastern Desert and was used to make small vessels.
| Fact 22 on Natural Resources: | Travertine: Travertine is a calcite rock, a variety of limestone, was also known as Egyptian alabaster. Travertine was carved into beads or statues and was particularly used to create the sacred tools used during the process of mummification and Canopic jars.
| Fact 23 on Natural Resources: | Serpentine: Serpentine was a dark green mineral found in the Eastern desert. Serpentine was used to create small vessels, funerary objects, talismans and amulets.
| Fact 24 on Natural Resources: | Rock Salt: The different types of rock salt that were common in the deserts of ancient Egypt were brine, natron, and soda which were used to flavor food or food preservation, to tan raw animal hides and were also used in medicine.
| Fact 25 on Natural Resources: | Peridot: Peridot also known as olivine is a light yellow-green semiprecious stone that was found in the Eastern Desert and the Western Desert. It was used to make talismans, amulets and jewelry.
| Fact 26 on Natural Resources: | Amazonite: Amazonite is the green Feldspar stone, one of the most precious stones of ancient Egypt. Amazonite was used to create small beads, statuettes, amulets, small vessels and inlays.
| Fact 27 on Natural Resources: | Milky Quartz: Milky Quartz is an opaque, milk-white variety of crystalline quartz, often with a greasy luster, that was abundant throughout Egypt. It was used to make talismans, amulets, pendants and funerary equipment.
| Fact 28 on Natural Resources: | Rock Crystal: Rock Crystal is a colorless transparent quartz and semiprecious gemstone. It was found in the Western Desert. Rock Crystal was used to make beads and small vessels but was also used to create the corneas of the eyes in statues and to decorate weapons.
| Fact 29 on Natural Resources: | Porphyry: Porphyry is a hard rock containing crystals, usually of feldspar or quartz and found in the mountain areas of the Western Desert. Porphyry was colored black, greenish black or purple and used to build columns and wall linings and to create small vessels.
| Fact 30 on Natural Resources: | Steatite: Steatite is a black gray material also known as "soapstone". It was a talc which was worked into ornaments, inlays, statues and bowls by grinding and polishing.
| Fact 31 on Natural Resources: | Sandstone: Yellow sandstone was found all throughout Egypt and was also sourced in Nubia. It was used to create great statues, reliefs and temples and was often painted. Sandstone is not as durable as limestone.
|
|
Ancient Egypt - Natural Resources Fact Sheet |
|

Natural Resources
Learning about the ancient Egyptians and Natural Resources inspires everyone to visit historical sites and undertake Egypt Travel and Tours to experience the wonders of this magical land at first hand. Many people choose to experience a tour of Egypt on a Nile Cruise stopping at the famous destinations and sites of Egypt such as the Pyramids of Giza and the Great Sphinx. The information and facts about the Natural Resources of Ancient Egypt will provide you with a great insight into Egypt and the legacy of the ancient Egyptians. Natural Resources |
|
|
|